A bollard is a short, sturdy, vertical post that is used in a variety of maritime applications. Originally used for mooring boats, bollards are now also used to control road traffic and to prevent automotive vehicles from colliding with pedestrians and structures. Bollards are commonly found on ships and docks, where they are used to secure mooring lines.
Bollards are typically made of steel or concrete and are designed to withstand the forces exerted by ships and other large vessels. They are often installed in groups, or clusters, to provide additional strength and stability.
Bollards are also used in conjunction with other mooring equipment, such as cleats and fairleads, to ensure that ships remain securely moored at all times.

In addition to their use in maritime applications, bollards are also used on land to control traffic and to provide protection against ram-raids and vehicle-ramming attacks.
They are commonly found in urban areas, where they are used to protect buildings, pedestrians, and other vulnerable structures from accidental or intentional collisions. Overall, bollards play an important role in ensuring the safety and security of ships, vehicles, and pedestrians alike.
Definition of a Ships Bollard
A bollard is a short post that is used to secure a ship or boat to a dock, quay, or pier. It is an essential piece of equipment used in the maritime industry to keep ships and boats safely moored in place. The term “bollard” originates from the nautical industry, where it refers to a wooden or iron post used for securing ropes for towing, mooring, and other purposes.
Bollards can be made of various materials, including wood, iron, steel, or stone. They are typically cylindrical or square-shaped and range in size from a few inches to several feet in height. Bollards are designed to be strong and sturdy, capable of withstanding the forces of wind, waves, and tides.
Ships bollards are generally located on a ship’s deck or on a quayside. They are used to secure the ship’s mooring lines, which are ropes that connect the ship to the dock. The mooring lines are essential for keeping the ship in place and preventing it from drifting away from the dock.
In addition to securing mooring lines, bollards can also be used for other purposes. For example, they can be used to secure cargo or equipment on a ship’s deck. Some ships also have bollards on board for wrapping and storing unused rope.
Overall, a ship’s bollard is a crucial piece of equipment that plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and stability of a ship or boat while it is moored at a dock or pier.
Types of Ships Bollards
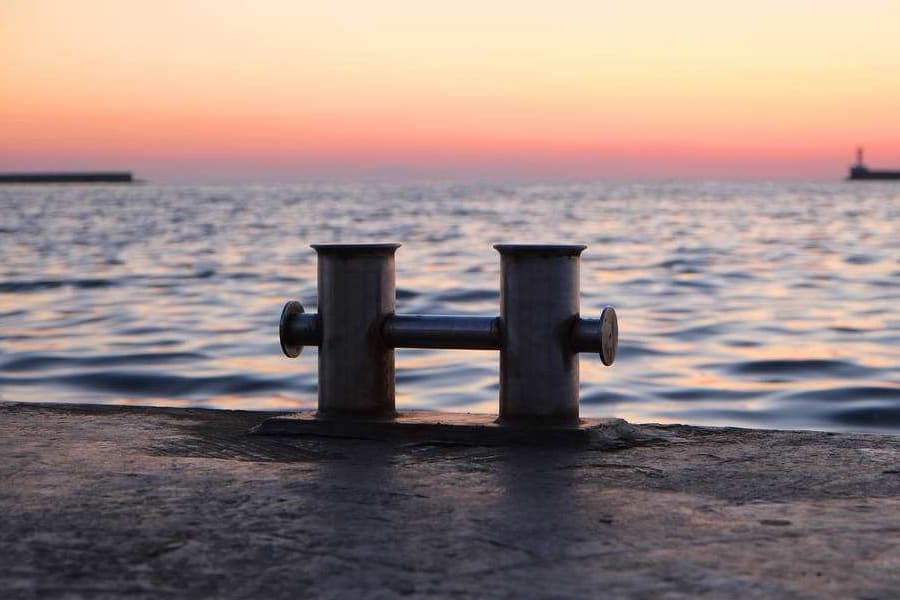
Ships bollards come in different types and designs to accommodate various mooring requirements. The most common types of ship bollards include Horn Bollards, Staghorn Bollards, Single Bitt Bollards, and Double Bitt Bollards.
Single Bitt Bollard
These bollards are typically characterized by a single cylindrical or slightly conical post. Single bitt bollards are often used for mooring boats or smaller vessels, such as recreational boats or small commercial vessels. The design is simple and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for locations that do not regularly service large ships.
Double Bitt Bollard
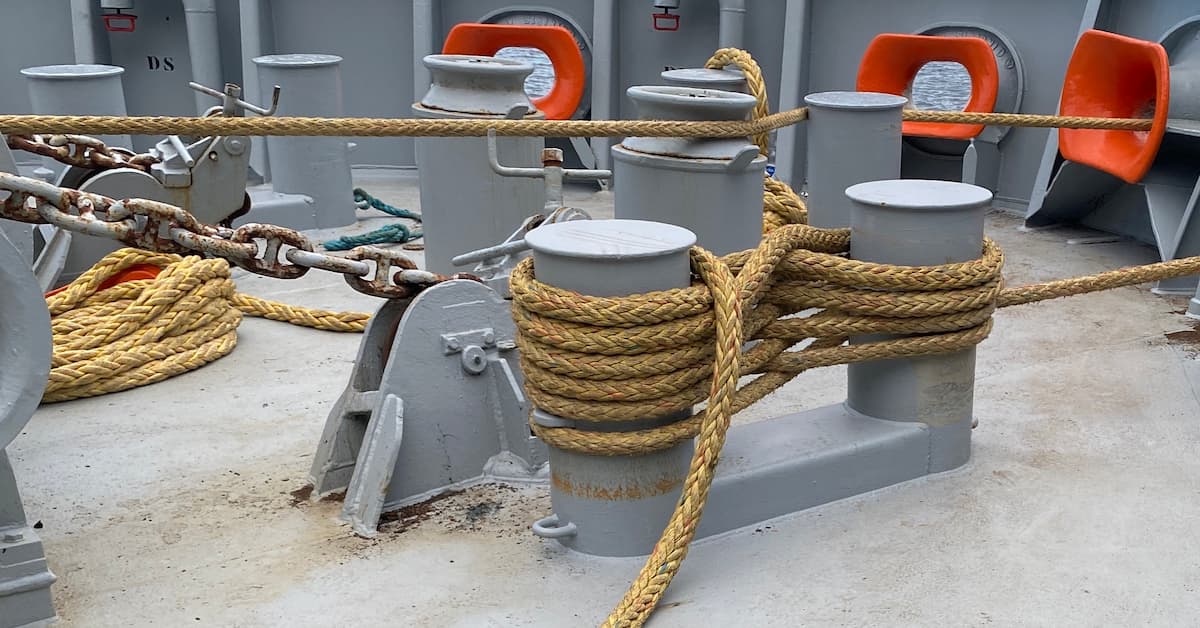

The Double Bitt Bollard is basically a single bitt bollard with two posts instead of one. This type of bollard is used to service larger ships, offering a greater area for securing mooring lines and distributing the force of a moored ship over a wider area.
Staghorn Bollard
The Staghorn Bollard is characterized by two horn-like protrusions extending from the top of the post. These ‘horns’ provide multiple options for securing mooring lines, which can be useful when servicing a large ship or when there is a need to secure multiple lines in different directions.
T-Head Bollard
A T-Head Bollard features a horizontal bar or ‘crosspiece’ on the top of the post, making it look like a ‘T’. This allows for even more options when securing mooring lines and is particularly useful for large ships with multiple or thick lines.
Horn Bollard
These bollards are characterized by a single post that splits into two ‘horns’ at the top, which resemble the antlers of a stag. They’re very versatile and can accommodate many different types of mooring arrangements. Their unique design makes it easy to quickly add or remove lines as needed.
Kidney Bollard
Named for its kidney-like shape, these bollards have a large, rounded top which allows for the securing of larger vessels with bigger mooring lines. The design provides an increased area of contact with the mooring lines, reducing wear and tear on both the line and the bollard.
R-Head Bollard
Similar to the T-Head Bollard, the R-Head Bollard has a top that curves around more, resembling an ‘R’. This design provides additional surface area for securing lines, which can be especially beneficial when servicing large ships.
Quick Release Bollards
These bollards are designed to rapidly release mooring lines in an emergency. They often feature a mechanism that can be manually or remotely activated to drop the lines. This type of bollard can be particularly important in areas prone to sudden changes in weather or sea conditions.
Cannon Bollard
Cannon Bollards are a traditional form of bollard that originated from the practice of burying old cannons to serve as bollards. While not typically used in modern docks, they can often be seen in older or historical areas. They are a testament to the innovative recycling practices of the past.
Pillar Bollard
Pillar Bollards are cylindrical in shape and are most commonly used in modern docks due to their simplicity and versatility. They’re designed to be strong enough to withstand the forces exerted by large vessels, but simple enough to be manufactured and installed easily.
Curved Dock Bollard
Also known as a “teardrop” bollard, this type is named for its unique shape, which is typically curved or teardrop-like. This design allows the mooring ropes to be placed at various points around the curve of the bollard, providing a more flexible mooring arrangement. The curved shape also helps to reduce chafing or wear on the ropes, as the pressure is distributed over a larger area rather than concentrated at a single point. This can be especially important when servicing large ships with heavy mooring lines, as the ropes can be subjected to significant forces.
Cruciform Bollard
Cruciform Bollards, as the name suggests, are shaped like a cross or a ‘plus’ symbol when viewed from above. This design gives them multiple points at which mooring lines can be secured, making them a versatile option for various types of vessels and mooring arrangements. The cross-shaped design also helps distribute the tension from the mooring lines evenly, reducing the risk of the bollard becoming dislodged.
Double Cruciform Bollard

The Double Cruciform Bollard is a variant of the cruciform bollard that features two cross-shaped posts instead of one. This design effectively doubles the number of points at which mooring lines can be secured, making it an ideal option for larger vessels or complex mooring arrangements.
The design also provides a higher level of stability and strength, making it suitable for use in areas exposed to high winds or strong currents.
Pillar Japanese Bollard

Pillar Japanese Bollards are a type of bollard commonly used in Japan and other parts of East Asia. They typically have a cylindrical shape with a flared top, and are often taller and narrower than many western-style bollards.
The flared top provides a larger surface area for securing mooring lines, which can help distribute tension more evenly and reduce wear on the lines.
Tricorn Bollard
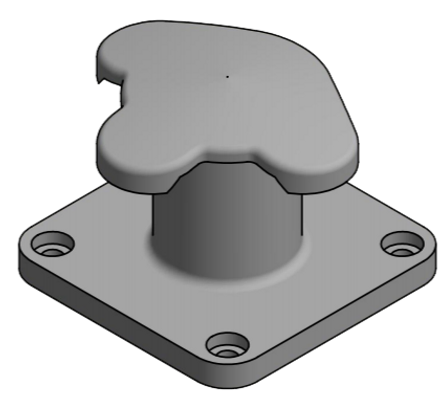
The Tricorn Bollard is named for its three ‘horns’ or points of contact, which give it a triangular shape when viewed from above. This design provides multiple points at which mooring lines can be secured, making it a versatile option for various types of vessels.
The triangular design can also help distribute tension from the mooring lines more evenly, reducing the risk of the bollard becoming dislodged.
Uses of Ships Bollards
Ships bollards are essential components of any maritime infrastructure. They are used for various purposes, including mooring, towing, and securing vessels. In this section, we will discuss each of these uses in detail.
Mooring
Mooring is the process of securing a vessel to a dock or pier. Ships bollards play a crucial role in this process. When a ship arrives at a port, it needs to be secured to prevent it from drifting away due to wind or water currents. This is where bollards come in. The ship’s mooring lines are attached to the bollards, which are then used to secure the vessel to the dock.
Bollards are designed to withstand the forces exerted by a ship. They are typically made of steel or cast iron and are anchored to the ground with concrete. The size and strength of the bollards depend on the size and weight of the vessel.
Towing
Ships bollards are also used for towing vessels. When a ship needs to be towed, a tugboat attaches a towline to the ship’s bollards. The bollards are then used to control the direction and speed of the vessel being towed.
Bollards used for towing are typically stronger than those used for mooring. They are designed to withstand the forces exerted by the towline and the weight of the vessel being towed.
Securing
Ships bollards are also used for securing cargo on board a vessel. When a ship is carrying heavy cargo, it needs to be secured to prevent the cargo from shifting during transit. Bollards are used to secure the cargo by attaching ropes or chains to them.
Bollards used for securing cargo are typically smaller than those used for mooring or towing. They are designed to hold the weight of the cargo without damaging the ship’s deck.
In summary, ships bollards are essential components of any maritime infrastructure. They are used for mooring, towing, and securing vessels. Bollards are designed to withstand the forces exerted by a ship and are crucial for ensuring the safety of vessels and their cargo.
Materials and Construction
Material Choices
Bollards can be made from a variety of materials, including wood, iron, steel, concrete, and stone. The material chosen for a bollard will depend on the specific application and conditions of the project site. For example, wooden bollards are often used in areas with a traditional or historic aesthetic, while steel or concrete bollards may be more appropriate for high-traffic areas or those requiring higher levels of security.
Design Considerations
When designing a bollard, several factors must be taken into consideration, including the size and weight of the vessel that will be moored, the type of mooring lines that will be used, and the expected wind and wave conditions at the site. Bollards must be designed to withstand the forces exerted by the vessel and the mooring lines, as well as any external factors such as wind, waves, and currents.
Construction Process
The construction process for a bollard will vary depending on the material chosen and the specific design requirements. For example, wooden bollards are typically constructed from solid timber posts that are cut to the desired length and shape, while steel or concrete bollards may be cast in molds or fabricated from pre-made sections.
Regardless of the material or construction method, all bollards must be securely anchored to the ground or other supporting structure to ensure they can withstand the forces exerted by mooring vessels. This may involve pouring a concrete foundation, drilling into the ground, or using specialized anchor bolts or other fastening methods.
In summary, the choice of material, design considerations, and construction process are all critical factors in the construction of a bollard. By carefully considering these factors and selecting the appropriate materials and construction methods, it is possible to create a bollard that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing, while also providing the necessary level of security and safety for mooring vessels.
Maintenance and Safety
Maintaining and ensuring the safety of bollards is crucial for the smooth and safe operation of a ship. Regular checks, safety measures, and potential risks should be taken into consideration to avoid accidents and damage to property.
Regular Checks
Regular checks should be conducted to ensure that the bollards are in good condition and functioning properly. The following checks should be made:
- Check for any visible damage to bollards, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose bolts.
- Ensure that the bollards are securely fastened to the deck and are not loose.
- Check that the bolts and nuts are tightened properly.
- Inspect the bollard’s base for any signs of wear and tear.
Safety Measures
Safety measures should be taken to ensure that the bollards are used safely and effectively. The following safety measures should be taken:
- Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with bollards.
- Use proper lifting techniques when handling heavy bollards.
- Ensure that the bollards are properly lubricated to avoid friction and wear.
- Follow proper mooring procedures and guidelines to avoid accidents.
Potential Risks
There are potential risks associated with the use of bollards. These risks should be taken into consideration to avoid accidents and damage to property. The following are potential risks:
- Overloading the bollards can cause damage to the ship’s structure and the bollards themselves.
- The ship’s movement can cause the bollards to break or become loose.
- Improper mooring procedures can cause the ship to drift away from the dock or collide with other vessels.
In conclusion, regular checks, safety measures, and awareness of potential risks are essential for the maintenance and safety of bollards. By following proper procedures and guidelines, accidents and damage to property can be avoided.
History of Ships Bollard
Early Usage
The use of bollards on ships dates back to the early days of seafaring. These devices were originally made of wood and were used to secure ropes for towing, mooring, and other purposes. A bollard was typically placed on the deck of a ship and was used to tie off a rope or line that was attached to a dock or other stationary object.
Over time, bollards evolved to become more specialized and were made from a variety of materials, including iron and stone. As ships grew larger and more complex, the need for more advanced bollards became apparent. In the mid-19th century, the first cast iron bollards were introduced, which could withstand the stresses of larger ships and heavier loads.
Modern Developments
Today, bollards are an essential part of any ship’s equipment. They are used to secure a vessel to a dock or other stationary object, as well as to provide a point of attachment for towing lines and other equipment. Modern bollards are typically made from high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum, and are designed to withstand the extreme stresses of heavy-duty marine operations.
In addition to their traditional use on ships, bollards have also found new applications in other areas. For example, they are often used as safety barriers in public spaces such as parks and plazas, as well as in industrial settings such as factories and warehouses.
Overall, the history of ships bollards is a testament to the ingenuity and resourcefulness of seafarers throughout the ages. From humble beginnings as simple wooden posts, bollards have evolved into sophisticated devices that play a critical role in the safe and efficient operation of modern ships.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of bollards?
Bollards are used to secure a ship to a dock or pier by anchoring the tow lines. They are typically short, sturdy structures made of metal and are found on the deck of a ship or on land.
What are the different types of ship bollards?
There are several types of ship bollards, including single bitt bollards, double bitt bollards, and cruciform bollards. Each type has a different design and is used for different purposes.
What is a mooring bollard?
A mooring bollard is a type of bollard that is used to secure a ship to a dock or pier. These bollards are typically found on the deck of a ship and are used to anchor the tow lines.
What is the difference between mooring bitts and bollards?
Mooring bitts and bollards are both used to secure a ship to a dock or pier, but they have different designs. Bitts are typically taller and thinner than bollards and are used for larger vessels. Bollards are shorter and sturdier and are used for smaller vessels.
What is the weight of a typical mooring bollard?
The weight of a typical mooring bollard can vary depending on its size and design. However, most mooring bollards weigh between 50 and 200 pounds.
What do bollards on a ship do?
Bollards on a ship are used to secure the vessel to a dock or pier by anchoring the tow lines. They are an essential part of a ship’s mooring system and are designed to withstand strong forces and heavy loads.
- Types of Gas Carriers as per IGC Code – April 22, 2025
- Wind-Assisted Propulsion Systems (WAPS): A Game Changer for Maritime Decarbonization – February 6, 2025
- 10 Boat Salvage Yards in California – January 25, 2025



