The bulbous bow is a game-changing innovation in modern ship design, enhancing both performance and efficiency. Dive into the fascinating world of the bulbous bow, an ingenious innovation that has transformed modern ship design.
Explore its hydrodynamic secrets, discover its myriad benefits, and unveil its real-world applications. This article will explore the intricacies of this fascinating feature, delving into its design, benefits, and real-life applications. Are you ready to embark on this captivating voyage?
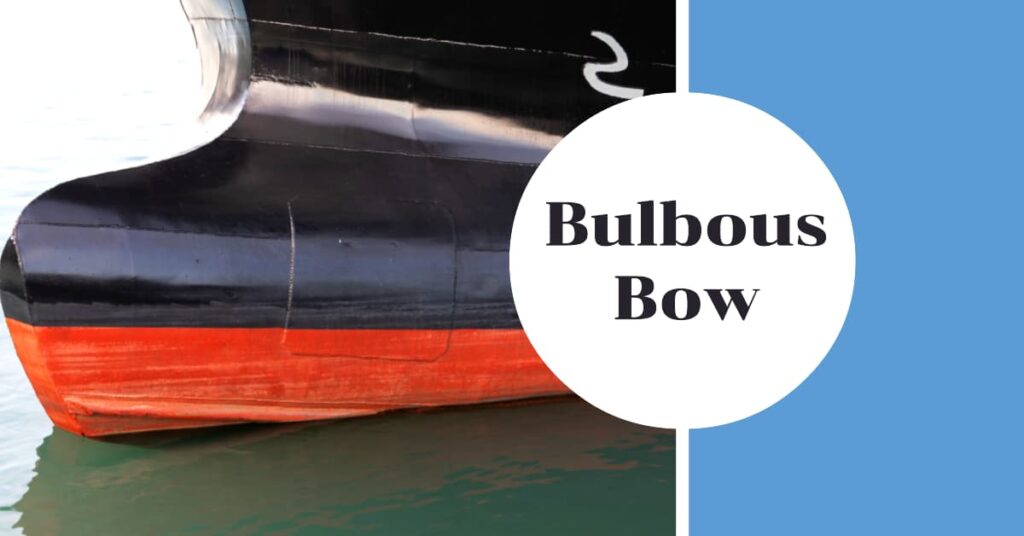
Understanding the Bulbous Bow
A bulbous bow is a protruding bulb at the front of a ship’s hull. Unlike a traditional bow, it extends underwater, disrupting the water flow around the vessel. First introduced in the 20th century, this innovative design reduces drag, saves fuel, and increases speed.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces drag, improves fuel efficiency, and increases stability |
| Design Principle | Interferes with the ship’s bow wave to reduce overall wave amplitude |
| Benefits | Enhanced fuel efficiency, reduced resistance, improved stability, and higher speeds |
| Common Applications | Cruise ships, cargo ships, and bulk carriers |
| Design Considerations | Ship size, displacement, operating speed, and hull shape |
How Bulbous Bow Works: Hydrodynamic Principles
The bulbous bow, a unique protrusion seen at the prow of a ship, is celebrated for the strategic hydrodynamic benefits it offers. As it stands, any ship traversing through the water inevitably generates waves. These waves, in turn, create resistance that can impede the ship’s speed and efficiency.
The prow of a ship, particularly when equipped with a bulbous bow, takes center stage in countering this problem. The unique design of the bulbous bow allows it to generate a wave of its own as the ship forges ahead. This wave produced by the bulbous bow is not just any wave; it is meticulously designed to intersect with the ship’s bow wave.
This intersection or interference orchestrated between the bulbous bow’s wave and the ship’s bow wave is a masterstroke in hydrodynamic engineering. It results in a significant reduction of the overall wave amplitude. Consequently, the drag or resistance experienced by the ship is markedly decreased.
This reduction of drag is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical implications that enhance the ship’s performance. With less resistance, the ship is enabled to glide more effortlessly and efficiently through the water. The bulbous bow, thus, contributes to not just the speed, but also the fuel efficiency of the ship, making it an integral part of modern naval architecture.
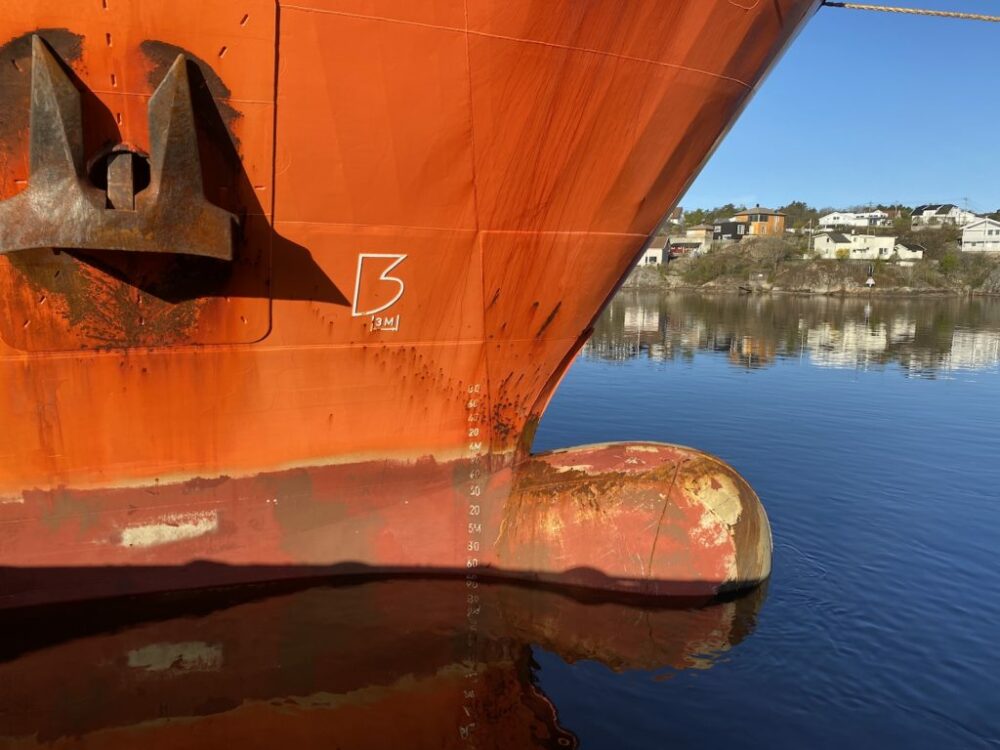

The Advantages of a Bulbous Bow
Ships equipped with a bulbous bow benefit from increased efficiency and performance. Let’s take a closer look at these benefits:
Reduced Drag
As mentioned earlier, the bulbous bow reduces drag by interfering with the ship’s bow wave. This reduction in resistance allows for smoother sailing and increased speed, making it a popular choice for various types of ships.
Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
With reduced drag comes improved fuel efficiency. The bulbous bow allows ships to travel at higher speeds with less fuel consumption. This not only reduces operating costs but also contributes to a greener maritime industry by lowering emissions.
Improved Stability
The bulbous bow can also improve a ship’s stability. By creating a more even distribution of water pressure, the vessel becomes less susceptible to pitching and rolling. This increased stability leads to a more comfortable experience for passengers and crew, particularly in rough seas.
Real-Life Examples of Bulbous Bow Use
Cruise Ships
The Titanic vs. modern cruise ships comparison reveals that bulbous bows have become standard for passenger vessels. The technology’s fuel efficiency and stability make it an ideal choice for cruise liners, which must balance comfort, speed, and environmental impact.
Newcastlemax Bulk Carriers
The Newcastlemax bulk carrier is another prime example of a vessel utilizing a bulbous bow. These ships transport vast quantities of dry bulk cargo, making fuel efficiency a top priority. The bulbous bow allows these vessels to save fuel while maintaining high speeds.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of Bulbous Bows
The bulbous bow has revolutionized the maritime industry, but it is crucial to ensure its effectiveness on a specific vessel. Engineers must consider several factors, including the ship’s size, displacement, and operating speed when designing the perfect bulbous bow. The right balance of these factors will maximize the bow’s benefits, optimizing the vessel’s performance.
Factors Affecting Bulbous Bow Performance
Ship Size and Displacement
A ship’s size and displacement play a significant role in determining the effectiveness of a bulbous bow. Larger vessels, like Kamsarmax bulk carriers and cruise ships, generally benefit more from a bulbous bow due to the greater resistance they encounter while moving through the water. However, smaller vessels can also benefit from a well-designed bulbous bow that is tailored to their specific dimensions.
Operating Speed
The operating speed of a ship is another essential factor in determining the effectiveness of a bulbous bow. Ships with higher operating speeds tend to benefit more from the drag reduction provided by the bulbous bow. However, it is crucial to design the bulbous bow to match the vessel’s typical operating speed range to ensure optimal performance.
Bulb Design and Shape
The design and shape of the bulbous bow directly impact its performance. A well-designed bulb will effectively interfere with the ship’s bow wave, minimizing resistance and maximizing fuel efficiency. Various bulb designs exist, each tailored to different vessel types and operating conditions. Naval architects must consider factors such as the vessel’s hull shape, operating speed, and displacement when designing the ideal bulbous bow.
The Evolution of Bulbous Bow Design
Over the years, naval architects have continued to refine bulbous bow design to maximize its benefits further. From the initial concept to today’s advanced designs, the bulbous bow has come a long way.
Early Designs
The first bulbous bows were relatively simple, consisting of a rounded protrusion at the front of the ship’s hull. These early designs offered some drag reduction but were far from the sophisticated designs seen today.
Modern Innovations
Modern bulbous bow designs have become more intricate and effective. Naval architects now use advanced computer simulations and testing to optimize the shape and size of the bulb for specific vessels and operating conditions. These modern designs offer superior performance compared to their early counterparts, leading to even greater fuel efficiency and speed.
Future Developments and Challenges
The bulbous bow continues to evolve as naval architects explore new ways to improve its performance. Some challenges and areas of future development include:
Environmental Impact
As the maritime industry focuses on reducing its environmental footprint, improving the bulbous bow’s design to further enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions becomes increasingly important. This focus may drive further innovation in bulbous bow technology.
Adapting to New Vessel Types
As new vessel types and technologies emerge, such as autonomous ships and electric propulsion, naval architects must adapt bulbous bow designs to accommodate these innovations. This adaptation could lead to the development of entirely new bulbous bow designs tailored to these cutting-edge vessels.
Balancing Performance and Practicality
The bulbous bow’s effectiveness depends on the right balance of factors such as size, shape, and speed. Future developments must continue to strike this balance while considering practical concerns such as manufacturing costs, ease of maintenance, and operational constraints.
In conclusion, the bulbous bow has revolutionized modern ship design, offering significant advantages in terms of performance, fuel efficiency, and stability. Its application across various vessel types, from chemical tankers and dry bulk carriers to cruise ships, showcases its versatility and effectiveness. As the maritime industry evolves, so too will the bulbous bow, continuing to shape the future of ship design and naval architecture.
Do All Ships Have A Bulbous Bow?
Not all ships have a bulbous bow. The use of a bulbous bow primarily depends on the ship’s size, type, and operating speed. While it is a common feature in many large vessels, such as cargo ships, cruise ships, and smaller vessels, certain ship types may not have a bulbous bow.
For some ships, the addition of a bulbous bow might not provide significant benefits in terms of fuel efficiency or performance, especially if they operate at lower speeds or have a specific hull design that renders the bulbous bow less effective. In these cases, a traditional bow design may be more suitable.
Ultimately, the decision to incorporate a bulbous bow in a ship’s design depends on the specific requirements and goals of the vessel. Naval architects consider factors such as the ship’s size, displacement, operating speed, and intended use when determining whether a bulbous bow would be an advantageous feature.
The Disadvantages Of The Bulbous Bow
Although the bulbous bow offers several advantages in terms of performance, fuel efficiency, and stability, there are some disadvantages associated with its use. Some of these drawbacks include:
- Design Complexity: Designing an effective bulbous bow requires advanced knowledge of hydrodynamics and naval architecture. The process can be complicated, as the bulb’s shape and size must be tailored specifically to the ship’s dimensions, hull form, and operating speed. This complexity can increase design and development costs.
- Manufacturing and Maintenance Costs: The construction of a bulbous bow can be more expensive and time-consuming compared to a traditional bow due to its unique shape and the need for specialized fabrication techniques. Moreover, maintaining a bulbous bow can be challenging, as it may require additional inspection and maintenance procedures, especially if it gets damaged.
- Reduced Performance at Low Speeds: The effectiveness of a bulbous bow is highly dependent on the ship’s speed. At low speeds, the bulbous bow may not generate enough wave interference to significantly reduce drag. In some cases, it may even increase resistance, reducing the overall efficiency of the vessel.
- Maneuverability Concerns: A bulbous bow can affect a ship’s maneuverability, particularly during slow-speed operations or in shallow waters. The bulb may increase the vessel’s turning radius or create additional water turbulence, making maneuvering more challenging.
- Incompatibility with Some Ship Types: Bulbous bows are not suitable for all vessel types. Smaller ships and certain specialized vessels may not benefit from a bulbous bow, as the advantages in performance and efficiency might be negligible or non-existent. Additionally, some ships may require different hull designs for specific operational requirements, making the bulbous bow less suitable.
While the bulbous bow offers many benefits for certain ships, there are disadvantages to consider. Naval architects must weigh the pros and cons of incorporating a bulbous bow in a ship’s design, taking into account factors such as vessel type, size, operating speed, and intended use.
- Types of Gas Carriers as per IGC Code – April 22, 2025
- Wind-Assisted Propulsion Systems (WAPS): A Game Changer for Maritime Decarbonization – February 6, 2025
- 10 Boat Salvage Yards in California – January 25, 2025



